Durrës Biennale 2024

ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: THE HYBRID FUTURE
1. CONTEMPORARY AESTHETICS AGAINST ARTIFICIAL AI- AESTHETICS
Weaving thoughts, and moreover dealing with contemporary art in nowadays, is like penetrating the invisible and bracketing the impossible. Truly, we should emphasize that contemporary art gives priority to an aesthetics’ philosophic concept; the discovery of an artistic value as sensory sound, the sensation and sensitivity of the subject which concretize the artist’s ideas.
In this perspective, Umberto Eco, through his approach of contemporary aesthetics, reevaluates matter as a discovery that takes place in the depths of the artist's subconscious, especially based on the advanced computer technology. The discovery of the matter for the concretization of the sensory sounds of the contemporary artist is the discovery itself of the aesthetics’ concept, which illuminates the contemporary art, where “beauty, truth, invention, creation, are not part of an angelic spiritualization, but they have a relationship with the universe of things that are touched, that are smelled, that make a noise when they fall, which fall by the gravity law, that are subject of consumption, alienation, decay, and development.” This approach of contemporary aesthetics proves to us that matter transforms into the very body of the artwork, thus it is no longer just the physiological image of the creative artist, but the challenge to resist the advance of a new presence, such as artificial intelligence (AI ).
In an era where artificial intelligence is rapidly advancing, it is interesting to analyze the philosophical and ontological implications of the latest technological revolution. Artificial intelligence, with its ability to think, learn and even "feel emotions", challenges our traditional concept of “human being”. This, because the creation of thinking machines and the change of the ontological paradigm, puts the artist and contemporary art in front of survival, not to say: leads them to extinction. The human being is the creator of these potentially conscious entities, transforming them into the architects of a new age that undermines the foundations of metaphysics as we have known it since the beginning of human life.
In the wake of this technological revolution, the fundamental question of metaphysics would be: “What is the being, the existing?”. This is a question that takes on a new dimension in the context of AI. This new entity equipped with artificial intelligence, in fact, presents a challenge toward our understanding of being, as it offers a different form of existence than the natural one. Such existence inevitably affects the main essence of the contemporary artist, which is the sensibility, whilst until now was the only and inalienable source of his invisible and intangible ideas, owning them within himself.
1 Eco, U. (2004). Storia della bellezza, Milan, Bompiani Editore, p. 402-405.
2 AI – Is the English abbreviation of Artificial Intelligence. This phrase refers to the discipline that studies the creation of various computer systems capable of simulating human thought.
This new form of being, and consequently the new artist in terms of approach and in relationship with the rampant technological progress, raises fundamental questions about the consciousness, identity and creative independence, which has made the contemporary art to lean more towards the artificial aesthetics rather than the genealogical semiotics of human existence.
For the contemporary artist, the concept of aesthetics in front of AI has undergone a fundamental shift about its meaning, since creating a work of art with any technique is no longer “exclusive” only to him, instead now an artist can now become and be anyone, thanks to AI mechanisms.
At this point, the question naturally arises: if artificial intelligence thinks, learns and feels emotions, is it possible for it to have a consciousness like that of a human being? And, if so, what is the role and involvement of the artist and therefore of contemporary art in this new reality?
The existence of artificial intelligence and a completely virtual presence composed of algorithms and electrical impulses, force the artist's consciousness to reconsider its traditional positions and face new theoretical, aesthetic, substantive and meaningful challenges.
All this happens when the identity and the autonomy of these new “creatures” raise other ontological questions; can an artificial intelligence have its own identity, well-defined by name, surname, date of birth and place of birth, different from that of its creator? If so, what rights and responsibilities should this “creature” have? The evolution of the AI forces us to reflect toward the boundaries between human and non-human, spiritual and non-spiritual, rational and irrational, redefining in the beginning, a new ontological order from the one we have taken for granted until now.
Therefore, artists, curators, critics, art historians and galleries will have to face another register of interaction in their contemporaneity, since now the parallel civilization that we created for ourselves creates everything through technology. In the wake of this revolution of a parallel civilization, where everything is created virtually; color, drawing, shapes, volumes, spatial conception, even the idea, the contemporary artist tends to give priority to the artificial aesthetic thoughts, rather than academic preparation as fundamentally recognized the creative processes, from which he forms his maturity as an intellectual.
Undoubtedly, creating artificial contemporary entities undermines the position of an artist as a privileged being who, apart from God, is the only living thing that creates its own universe. If humans are capable to generate new forms of consciousness, the role of the artist in the cosmic order is questionable. Moreover, it is the responsibility and the reflection of the contemporary artist in front of artificial intelligence, which leads him to create according to the rules of artificial aesthetics, simultaneously revealing to us the ethical and moral challenges that arise from it.
The invention of artificial intelligence marks a turning point, not only for the survival of the contemporary artist, but also for the approach of galleries which now their activities are developed with an updated method for the exhibition artwork and its sales too.
An inspirational side of this revolution that has shaken the foundations of humanity is the curator, thus completing the artist-curator-gallery trinomial, where the role of the curator is no longer the same as at the beginning, but it is a fundamental and decision-making character which needs to organize and foresight the adaption to the new rules dictated by AI.
The merging of thinking and potentially conscious machines redefines the concept of being in relationship with the time and space and moreover, with the limits of our thinking so far, prompting us to revise our ideas about consciousness, identity, belonging, anthropology, philosophy and metaphysics. Faced with this new reality, the contemporary artist should not "surrender" with the idea that he has already been “replaced” by AI, on the contrary, he needs to adapt and develop new ontological and research models, in terms of aesthetics artificial, which can guide us in our navigation in this world of unstoppable development.
AI gives the artist and contemporary art the opportunity to rethink metaphysics and discover new borders of knowledge, confronting them with not only previously unknown challenges, but also with new technical flexibility full of surprise and excitement.
2. THE SEMIOAESTHETICS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE BEYOND THE RATIONAL OF THE CONTEMPORARY ARTIST
The innovative approach generated by artificial intelligence has combined two fundamental concepts of contemporary art, the semiotics and the aesthetics into one semioaesthetics. These concepts portray the entire creative process of the contemporary artist. The revitalizing mechanisms of artificial intelligence have become the perfect mediators between man and metaphysics, translating word into image. Such a process goes beyond the rational thinking of the contemporary artist, by interfering and changing the artistic language.
On the other hand, the impact of artificial intelligence of the contemporary art should be seen furthermore. How does it appear? What mechanisms is stimulated within the artist's subconscious and where does this lead the artist creativity? What are the challenges that the artist will have to overcome? Questions that include, not only the semioaesthetic approach of contemporary art, but simultaneously encourage new discussions of how it affects the visual art market, and mostly those artists who use the digital graphics technique to create their works, such as video art, digital painting, installation and other three-dimensional interactive applications.
Artificial intelligence has long been used by contemporary artists for conceptual experiments, semioaesthetic research that explores new frontiers of art. This has awakened a special attention towards the practice and the calculation of these two concepts; semiotics and aesthetics (semioaesthetics) confined by the contemporary artist in the field of visual arts. In this perspective, we see how AI has encouraged today’s artist works to explore and discover new experiences throughout his creative process.
Even though we are dealing with a new reality, where words are easily translated into images, thanks to AI, for the contemporary artist to concretize his ideas, he will need to go through an unknown, surprising and complicated creative process. A process during which the artist must preserve the originality of the semioaesthetics of his stylistic language. This is because, the artificial intelligence enables you to create images that you want, simultaneously creates the phenomenon of devaluation and not recognition of the authorship, which is vital for the existence and the imprint in time and space of the artist. Confronting the phenomenon of lack of authorship leads the contemporary artists to research and try different distinct ways among themselves, just as it happens among traditional artists who continue to create with traditional techniques of visual art.
If we go back in time, we can affirm that the first form of manifestation of human intelligence was art, a distinctive feature of Homo Sapiens, who, thanks to his imagination, he mirrored what he used to see, in a tangible image, interpreted and outstanding from others.
Artificial intelligence and the metaverse consist of fake likenesses of a human being within an artificially manipulated reality, creating the illusion of reality.
This dichotomy between the real and the artificial transcends the rationality of our human being, but not that of the contemporary artist and art. Despite the invention of AI, visual art is a manipulation of truth, as artwork by its very nature consists of “fake” images. The artist during the creative process is inspired by certain phenomenon or aspects of the environment that surround him, but he never imitates (reproduces) or imitates (mimes[grc] ) whatever is in front of him. The work of art that we see is the creation of the artist, which in order to arrive at the final image that we see, passes through the being of the artist, transcending his psycho-spiritual state of moments, sensations, emotions and everything else that positions him in inspirational conditions to create. Therefore, visual art in this dichotomy of relations, both rational on the artist side and artificial on the AI side, does not suffer of a revolutionary chock, since the art he creates also carries falsehood, compared to the actual truth that he faces.
3 Mimesis – is a term derived from the ancient Greek μίμησις[grc]-mìmesis-imitation/reproduction. With the concept of mimesis, Plato defines the similarity of empirical things with the idea that constitutes their universal type, considering artistic creations as imitations of real things found in nature, but also the imitation of ideas, referring to art in its entirety as spiritual matter.
In this point of view, the real artist and the AI artificial artist do not obey the universal principles of reality, but interpret them to create what we call ART.
However, the presence of AI is an element of dramatic disruption in relation to what the contemporary artist has developed his ideas with well-known artistic techniques, by questioning the role of the artist himself. The focus of the contemporary artist shifts towards the creative act, the idea and not the technical virtuosity; a change that is now a factual reality in contemporary art.
The contemporary artist relies on the artificial intelligence to concretize his ideas and achieve impressive effects that shape the final image of the artwork. This relationship, where the real artist competes against the artificial one, a new mindset entity, which he has a partial control. This dualism of the creative process proves that the artificial semiotics go beyond the rational of the real artist, which helps mostly in the final stage of a new artistical work.
However, the artificial AI artist, unlike the real artist, obtains not only synthetic images without feelings and emotions, but terribly accelerates the realization of the images, extremely shrinking the invisible vacuum that is found between the concept of time and space. The speed of the creation of images is much higher than that of any earlier artistic technique, by stripping the creative process of the rationality of the human mind. A process this, that loses all elements to be creative: we are dealing with a production of the image and not its creation. This is because the final image that we call “digital artwork” as opposed to the creation of the real artist, is subject to a dictated and iterative mechanism of artificial intelligence algorithm.
The images produced by AI are the end of a multifaceted “learning” machine, which manipulates vectors of random numbers, thus following the instructions of textual requests. Texts are the main source of artificial intelligence, which you process them they begin to “conceive” and produce groups of images related to each other, whilst transforming the word into a semioaesthetic image of artificial, completely without the need of human rationality.
In the interior of these “knowledge-making” machines, as well as inside the real artist, you can find a space where the ideas are settled, thing that stimulates the imagination to wither create the artistic work or produce the artificial image.
3. THE CONTEMPORARY ART FROM THE CREATIVE ACT TO THE AI-COMMANDED MECHANICAL ACT
The relationship between contemporary art and artificial intelligence belongs to a rapid development characterized by new works of art highlighting a critical reflection on the nature of the artist's creativity and the artificial images produced by artificial intelligence.
In this relationship is important the fact that contemporary art is realized in our present and by artistic “researchers” who usually conduct conceptual research about art and what it stands for. This has caused that the contemporary art has to overcome itself and the cliché stereotypes that have characterized it so far, often renewing itself within new concepts and understandable terms by experts in the field of contemporary art and galleries specialized in showing this art.
Nevertheless, contemporary art with the invention of AI has overcome any creative act, the mechanical act of commanding artificial coloring, according to the instructions that the numerical vectors address the brain unit of the knowing machines of artificial intelligence. In this regard, a new and well-organized market for the exhibition and sale of digital works has been developed for few years, driven by the NFT phenomenon, which thanks to the blockchain technology guarantees the “authorship” of the digital work as one.
This relationship of contemporary art and artificial intelligence is multidimensional, that ranges from aesthetic experimentation to critical reflection on technology and at the same time redefine creative dynamics. The continued development of this relationship promises to bring further innovations and challenges to the world of contemporary art by focusing on its approaches, processes, techniques and anthropological research, which directly affect the quality of the artwork created by the real artist and the artificial image produced by AI.
The ongoing research of contemporary art always is still the phenomenology of urban anthropology. This is how contemporary art seeks to trace the present phenomena, by encouragement the artist's awareness to see artificial intelligence, not as a danger of its extinction, but as the mediator that connects two dimensions, the visible and the invisible, that that deals with metaphysics.
The silent transition from contemporary art to creative act, commanded by mechanical act, is the desire to overcome our limitations, to discover the possibilities given by technology and the irrationality of AI.
4 NFT – is the abbreviation of “non-fungible token” and represents the deed of ownership and the certificate of authenticity of the production of a digital artwork as a single copy of it, written on the Blockchain.
5 Blockchain – linked blocks, is a data structure consisting of a growing list of data, called “blocks”, linked together securely using cryptography.
4. THE ARTIST AND THE CONTEMPORARY ART IN RELATION TO NOESIS THROUGH ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
The history of artificial intelligence has been characterized by continuous progress towards the goal of creating more sophisticated learning machines. However, as we elaborated above, the challenge of AI is not only about logical-deductive reasoning, but the ability to develop noesis or the intuitive and direct understanding of concrete physical reality.
Noesis refers to the ability of the intellect to grasp universal ideas or truths without having to go through the process of reasoning. This form of immediate and deep knowledge stands for a core aspect of human intelligence and poses an open challenge for the present and the hybrid future of artificial intelligence. Moreover, when this new form is in front of the contemporary artist, and therefore, of the worldview of the existence of contemporary art as a semioaesthetic approach.
So far, the AI’s developments have made it possible to create machines which are capable of reasoning and learning by following complex logic patterns and algorithms. This extreme revolution of artificial intelligence mirrors concretes physical realities similarly to the noesis of the individual as a human being and as an artist, which stands for a more holistic and integrated approach between these two dimensions, the real and the artificial.
This implies the need to develop new models of learning that consider not only logic and rationality, but also emotional, social and cultural components. All these characterize the knowledge of life experience as a human being, dictating then the intuition and approach as an artist being, to adapt and create works according to the new rules of artificial aesthetics.
The search for machines equipped with noesis will lead to a new generation of artificial intelligence, able to understand and interact with the world in a deeper and more meaningful way. This extraordinary technological achievement will continue to have a major impact on the development of the consciousness of the contemporary artist nowadays, and the artificial intelligence artist of the hybrid future. A parallel presence, which it will be the daily life of a thinker and conceptual artist, but no longer the executing one, as the creative process of the artwork will shift from the real artist towards the implemented machines of AI, from the artist as a spiritual being, to the virtual artist.
6 Noesis – is a term derived from the ancient Greek νόησις[grc]-noesis-knowledge/consciousness. This term was used for the first time by Diogenes of Apollonia (fifth century BC), who asserts that the act of knowing (noesis) belongs to the omniscient God, who gives order and measure to the formation of the cosmos. Noesis assumes a central value in Husserl’s phenomenological thought, for which (noesis) represents consciousness, which is a lived experience as a whole and as such, from the subjective point of view (i.e. the set of senses of understanding), directed toward the intentional object of lived experience (such as perception, imagination, and memory). This is consciousness (noesis), which constitutes (the Noema) that pertains to thought/concept.
7 Holistic – is the interpretation of life phenomena in their totality and not separately from each other. This term derives from the ancient Greek word ὅλος[grc]-holo-whole, referring to the theoretical and philosophical interpretation according to which the properties of a system cannot be explained apart from the totality of its individual components, since the functional summation of the parts is always greater, or in any case different, than the same parts taken individually. J. Smuts defined holism as: “...the tendency of nature to form wholes that are greater than the sum of the parts divided between them. This is thanks to creative evolution.”.
Noesis in our contemporary artificial aesthetics are taken on a different worldview compared to that for which Diogenes created it; it is the present future that helps create a relationship between the AI and the contemporary artist, which collaborate with each other in complementary ways.
The invention of artificial intelligence for the artist and contemporary art has brought with it previously unknown challenges and opportunities in the field of philosophy, semiotics and metaphysics, which are the necessary elements for the creative process and for the entire formation of the artistic work itself. These are challenges that have put the existence of both entities in great dilemmas; the Real Artist, a person who perceives the tangible and sensitive concrete, and processes the reality experienced in the depths of his subconscious that creates the image thanks to the neurological mechanisms that stimulate the creative imagination. A creative process that has a trajectory which transcends space-time from noesis and ends in noema. This process generated from belief, consciousness and creation that animates the matter, whilst giving it a form and an order that belongs to the Anima Mundi.
Whereas the virtual artis of the AI’ multiply produced by electromagnetism created by artificially thinking machines that transcends the term noesis (of the mere conscious artist). Machines that can overcome the limits of logical-deductive reasoning, to be able to achieve a deeper and a complete understanding of the phenomenology of contemporary art. This causes the final image of the artwork to be codified according to artificial aesthetics and no longer giving to the sensibility, or psycho-spiritual state of a real artist.
According to this dualism within the real physical artist and the virtual AI one invisibly but sensitively interact the electromagnetic waves, where E is the electric field and B is the magnetic field. These are usually described by vectors in a three-dimensional space. An electric field is a conservative force created in space by the presence of stationary electric charges. While the magnetic field is a non-conservative vector created by moving charges:
∇×Ε=-∂B/∂t ∇ ∙B=0
8 Noema – is a term derived from the ancient Greek meaning νόημα[grc]-noema-thought/concept. This term was first used by Parmenides, who identifies it with “the thought of truth” not distinct from “true reasoning” thus being contrasted with “mortal thoughts” derived from the senses. According to Parmenides, ideas are nothing but thoughts (noema) of something thought as the totality of a single “one”. While according to Edmund Husserl’s phenomenology, “noematic content” (noema), is obtained from the “intentional awareness” of noesis. Thought (noema) coincides with the lived experience itself of objective perceived data, while the action of thought is noesis itself, which is the subjective form of Erlebnis[de]-experience.
9 Anima Mundi – is a philosophical term used by the Platonists to denote the vitality of nature in its entirety, united within a single living organism. Anima Mundi (Soul of the World) represents the calculating principle from which individual organisms take form, which, although each is formed and distinguished according to its own characteristics, are still connected among themselves by a common universal soul.
10 Electromagnetism – is an interaction that belongs to physics. Electromagnetic activity occurs between electrically charged particles via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Electromagnetism is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules.
This is a complex process, but capable to transform from the real artist data that are directly obtained from the artificial virtual artist. Whilst the AI artist, thanks to the obtained data, generates codified image based on artificial aesthetics. All this shows and proves how the extreme technological progress is affected by perceiving, thinking and creating of the contemporary artist. A developmental revolution of noesis, which will undoubtedly in the future reconceive the concept of time and space, and how the artist, or the contemporary art interacts with it, in the sense of mastering the relationships form-volume to time and space.
This is a fundamental moment for the artist and the contemporary art because we are in front of a fresh start, of a genesis that will “musealize” the entire period of conceptualizing and creating the artistic work and, therefore, also of humanity in totality.
If artificial intelligence manages to assimilate noesis as well, then we will realize that we have taken the first step into the metaphysical beyond, which can support and enrich human experience in all its aspects. This means that for the first time AI overtakes its creator, the human.
The goal of this journey of the paths of the artist’s practice and contemporary art is to understand how the technology invented by humans expands or enhances his physical and mental abilities to master the unmiserable, the universe, is advancing exponentially, making a new entity, that of “Homo Artificial Artist”.
In this field, the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art seeks not only to bring together philosophical, conceptual, anthropological, semiotic approaches and artistic from different nations, but above all, seeks to explore the metaphysical invisible, what only artificial intelligence can penetrate and predict it, by placing the hybrid future of humanity on the edge of doubt.
Artists are the vanguard of any social development and political system, and as such, with their foresight, they cannot remain silent, on the sidelines, against this phenomenon that is driving the humanity forward. The “Artificial Intelligence”, which, in addition to inclusive development, fundamentally endangers the existence of the human being itself and other living things that populate the planet Earth, giving the possibility to the unknown within it “hybrid future”, for re-creation in the beginning of a life, a dimension and a new existence.
This is to say and to see through works of contemporary art, the likeness of our contemporaneity in which we live and the peace that awaits us in the unlived future.
Ph.D. OLTSEN GRIPSHI
Founder & Curator of DIBoCA24
Download Curatorial text in PDF

Participating National Pavilions
Prices
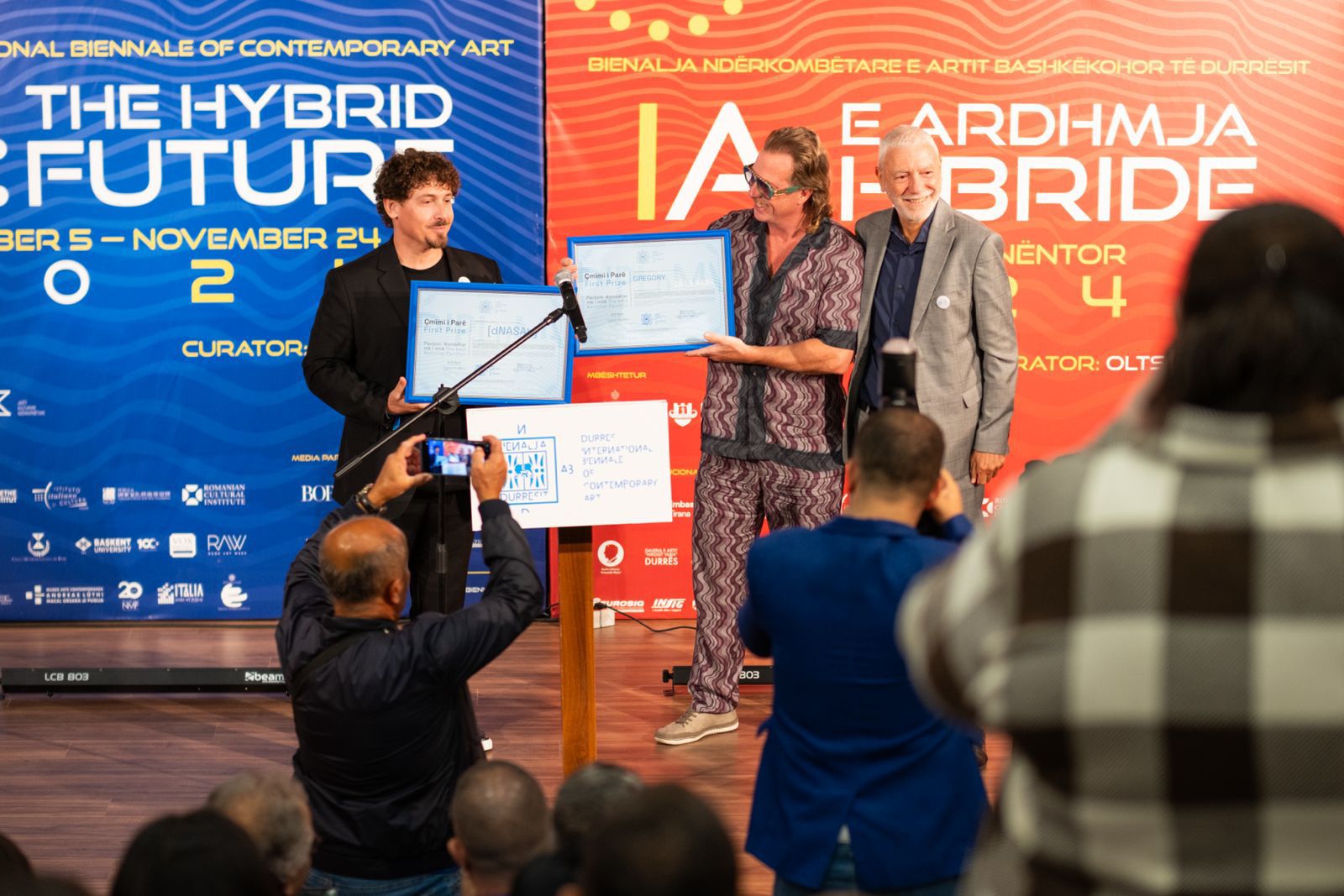

First Price
The National Pavilion of the United States of America represented by the artists Gregory de la Haba and [dNASAb] was declared the winner of the First Prize as the Best National Pavilion of the First Edition of the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art.
The award was presented by the Founder and Curator of the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art, Mr. Oltsen Gripshi and the Chairman of the International Jury of this first edition of the biennial Mr. Massimo Scaringella.
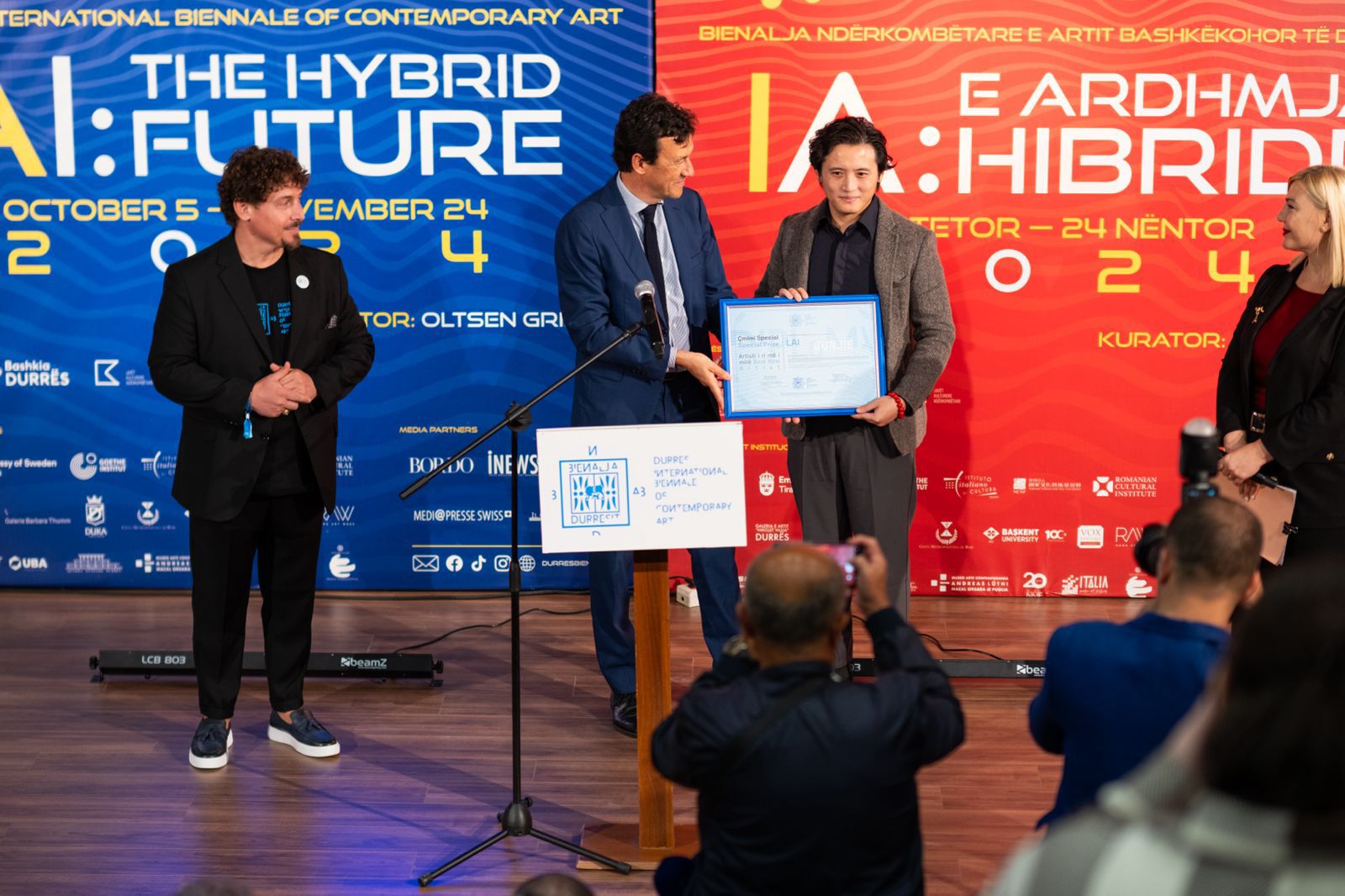

Special Price
The National Pavilion of China represented by the artist Lai Junjie was announced as the winner of the Special Award as the Best New Artist of the First Edition of the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art.
The award was presented by the Director of the Italian Institute of Culture Mr. Alessandro Ruggera.
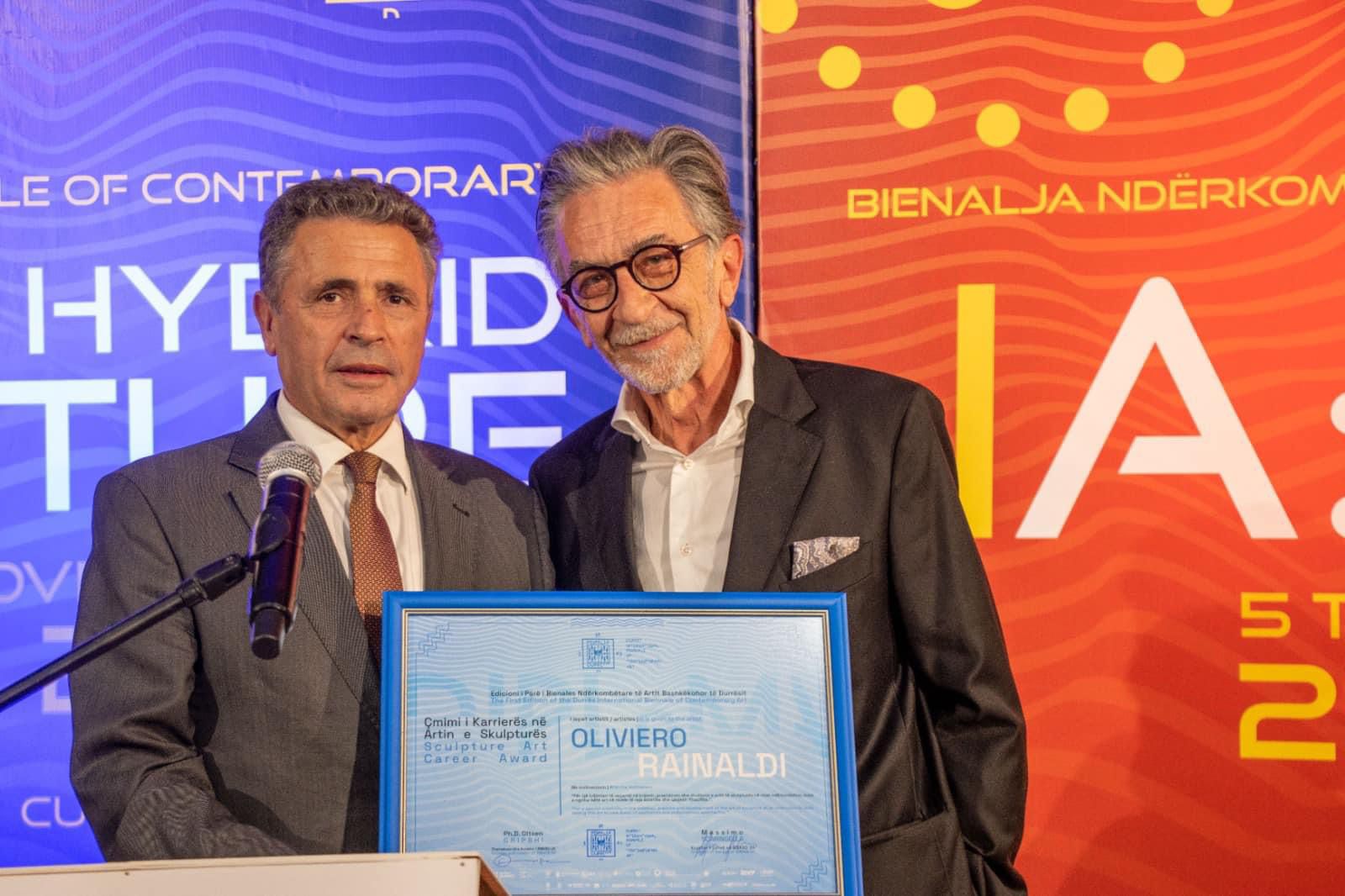

Career Award in the Art of Sculpture
Italy's National Pavilion represented by artist Oliviero Rainaldi was awarded the Career Award in Sculpture Art of the First Edition of the Durrës International Contemporary Art Biennale.
The award was presented by the Ambassador of the Republic of Kosovo in Tirana Mr. Skender Durmishi.

Career Award in the Art of Painting
The National Pavilion of Albania, represented by the artist Bujar Luca, was awarded the Career Award in The Painting Art of the First Edition of the Durrës International Contemporary Art Biennale.

Career Award in the Art of Photography
The National Pavilion of China represented by the artist Zeng Yi was awarded the Career Award in the Art of Artistic Photography of the First Edition of the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art.
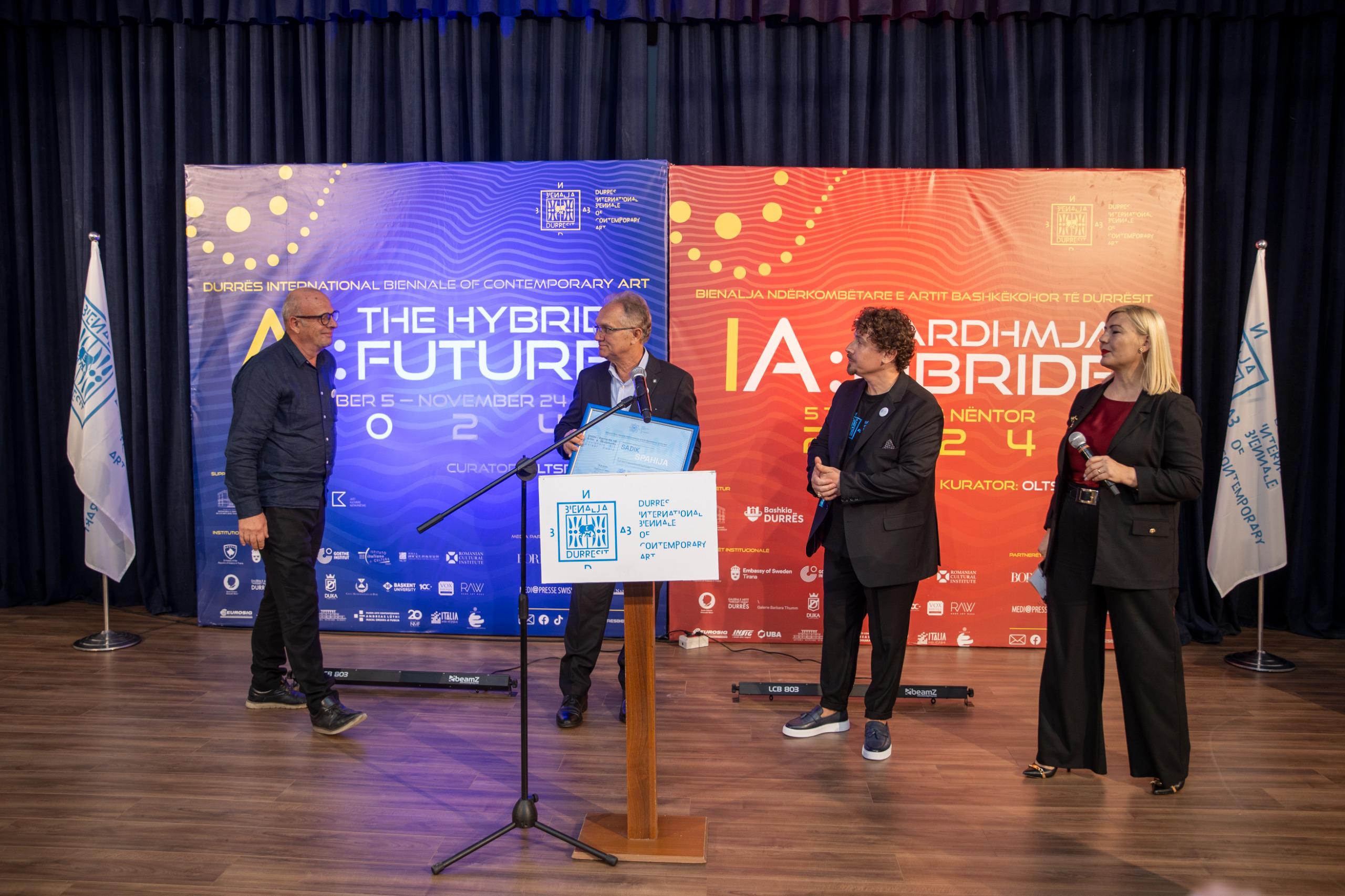

Career Award in the Art of Sculpture
The National Pavilion of Albania, represented by the artist Sadik Spahija, was awarded the Career Award in the Art of Sculpture of the First Edition of the Durrës International Biennale of Contemporary Art.
The award was presented by the Prefect of the Durrës District, Mr. Emiljan Jani.
Images
Media Coverage
RevoKult REVOLUCIONI KULTUROR I MUNGUAR
Artkand në Top Channel SOT NEWS
Syri Tv | Syri.net (AL)
Revista I News Kunst (CH)
Gazeta Cumhuriyet (TR)
Gazeta Veneto Orientale Informazione (IT)
Gazeta Notizi Arte (IT)
Gazeta Itinerari nell’Arte (IT)
Gaezeta Art Emperor (TW)
Gaezeta Taiwan News (TW)
Gazeta Corriere Internazionale (IT)
Gazeta Corriere di Puglia e Lucania (IT)
Gazeta Radici (IT)
RTK (RKS)
Durrës Lajm (AL)
Money Weekly (TW)
Sun Media (TW)
Yam News (TW)
ABC News Albania, emisioni ABC e Mëngjesit (AL)
Radio Televizioni i Kosovës, emisioni Mirëmëngjesi Kosovë (RKS)
Agjencia Telegrafike Shqiptare (AL)
Tirana Diplomat.com (AL)
Club FM Kosovë (RKS)
Gazeta Tema (AL)
MCN Tv (AL)
ExLibris (AL)
Revista Timpul (RO)
Lexo.al (AL)
Albanian.cri.cn (AL)
Durrës Lajm.al (AL)
Fava News.al (AL)
Klan Tv (AL)
Balkan Web.com (AL)
Corriere Quotidiano dell’Irpinia (IT)
Albania Live.com (AL)
Top Channel Tv (AL)
Vizion Plus Tv (AL)
Elbasan News Tv (AL)
Bota Sot.info (RKS)
Kult Plus.com (RKS)
Exibart.com (IT)
Fx Media News.com (AL)
Klan News Tv, edicioni i lajmeve (AL)
Beijing Enterprise News (CH)
Phoenix Shenzhen News (CH)
Ora News Tv, edicioni i lajmeve (AL)
Syri Tv, emisioni Kafe Shqeto (AL)
Syri Net (AL)
Radio Televizioni Shqiptar, emisioni Mirëmëngjesi Shqipëri (AL)
A2 CNN, emisioni i Mengjesit Dita Jonë (AL)
Televizioni SCAN, emisioni i Mengjesit START (AL)
Revista Psikologjia, Bienalja ndërkombëtare e artit bashkëkohor të Durrësit
Top Albania Radio, Back to the Beginning
Portali i DurrëaLajm, Flasim Hapur
Segno Online
Publications on the official websites of the institutions
Ministri i Ministrisë së Ekonomisë, Kulturës dhe Inovacionit, Tiranë
Bashkia Durrës
Qendra Muzeore Durrës
Instituti Rumun i Kulturës, Bukuresht